Call For Instant Quote
Call For Instant Quote

SOLAR + HOME ENERGY AUDIT: Uncover Hidden Savings, Boost Efficiency & Increase Home Value
A home energy audit reveals inefficiencies and opportunities to save, and pairing it with solar power maximizes the benefits. Here are 25 potential reasons why your electricity bill might be increasing (plus 20 more potential taxes and fees):
Increased Usage: Seasonal changes, like using air conditioning in summer or heaters in winter, can cause spikes in usage.
Rate Hikes: Utility companies may increase electricity rates without significant notice.
Inefficient Appliances: Older or less efficient appliances consume more electricity.
Phantom Loads: Electronics and appliances left plugged in continue to draw power even when turned off.
Higher Occupancy: More people in your home may lead to increased usage of lights, devices, and appliances.
New Appliances: Adding energy-intensive appliances (like a new hot tub, pool pump, or second refrigerator) increases consumption.
Faulty Appliances: Malfunctioning appliances can draw more power than necessary.
Improper Insulation: Poorly insulated homes lead to energy loss, causing heating or cooling systems to work harder.
Extended Device Use: Increased time spent at home (e.g., remote work) can lead to higher usage of electronics and appliances.
Running HVAC Systems Constantly: Keeping heating or air conditioning on for extended periods, especially at high settings, increases costs.
Leaking Ductwork: Damaged or leaking air ducts cause HVAC systems to work harder.
Dirty Filters: Dirty HVAC filters reduce efficiency, leading to increased energy usage.
Inefficient Lighting: Using incandescent or halogen bulbs instead of energy-efficient LEDs consumes more electricity.
Frequent Use of High-Powered Appliances: Appliances like ovens, clothes dryers, and dishwashers use significant energy.
Old Water Heater: Inefficient or poorly maintained water heaters consume more power.
Increased Hot Water Use: Using more hot water (e.g., longer showers) results in higher electricity bills if you have an electric water heater.
Overcharging Devices: Leaving phones, laptops, and other devices plugged in after charging increases usage.
Outdoor Lighting: Leaving outdoor lights on all night or using non-energy-efficient lighting increases costs.
Poor Thermostat Management: Failing to adjust the thermostat when away or during the night wastes energy.
Electric Vehicle Charging: Charging an electric vehicle at home significantly increases electricity usage.
Pool Pumps: Operating a pool pump for long hours or with inefficient settings adds to electricity bills.
Electric Space Heaters: Space heaters are energy-intensive and can spike electricity costs if used frequently.
Growth of Smart Devices: Adding more connected devices (like smart speakers, cameras, or other IoT gadgets) increases overall consumption.
Peak-Time Usage: Using appliances during peak hours when electricity rates are higher.
Twenty (20) Additional Charges That Could Be On Your Bill: Utility bills often include several additional charges beyond the rate per kilowatt-hour (kWh) for electricity consumed.
These charges can vary by utility provider and region, but common items include:
Delivery Charges: Covers the cost of transmitting electricity from power plants to homes and businesses via power lines, substations, and other infrastructure.
Distribution Charges: Fees for maintaining and operating the local distribution network that delivers electricity to customers.
Fixed Customer Charge: A flat fee to cover administrative costs, such as billing, customer service, and account management.
Demand Charges: For commercial or industrial users, this fee reflects the highest level of electricity demand used in a billing period.
Energy Adjustment or Fuel Charge: Adjustments based on fluctuations in the cost of fuel used to generate electricity, such as coal, natural gas, or renewable energy sources.
Renewable Energy Surcharge: A fee to support investments in renewable energy projects or to comply with renewable energy mandates.
Capacity Charges: Covers the cost of ensuring there’s enough generation capacity to meet peak demand.
Regulatory Charges: Fees imposed by government regulators for policy mandates, environmental compliance, or energy efficiency programs.
Transmission Charges: Costs associated with the long-distance transmission of electricity from power plants to local distribution centers.
Metering Charges: Fees for installing, maintaining, and reading electricity meters.
Service Connection Fees: Charges for setting up or reconnecting electricity service, particularly for new accounts or after service disconnection.
Taxes: Local, state, or federal taxes may be added, such as:
Sales tax
Utility-specific taxes
Energy conservation taxes
Franchise Fees: Payments made by the utility company to local governments for the right to operate in the area, often passed on to customers.
Environmental Compliance Charges: Costs incurred by utilities to meet environmental regulations, such as pollution control or carbon reduction efforts.
Time-of-Use Surcharges: Additional charges for using electricity during peak demand periods.
Grid Maintenance Fees: Costs for maintaining and upgrading the electricity grid.
Storm Recovery Charges: Temporary fees to cover costs related to restoring service after major weather events or natural disasters.
Late Payment Fees: A penalty for not paying the bill on time.
Deferred Payment or Budget Billing Adjustment: Charges or credits related to equal payment plans or payment deferrals.
Public Benefit Charges: Fees supporting public programs like low-income assistance, energy efficiency initiatives, or educational outreach.
Solar energy not only reduces your reliance on the grid but also locks in savings and shields you from unpredictable rate hikes. By investing in solar, you create a cleaner, more efficient home while securing long-term financial and environmental rewards. Take control of your energy future—go solar today. Book your free consultation with us today.
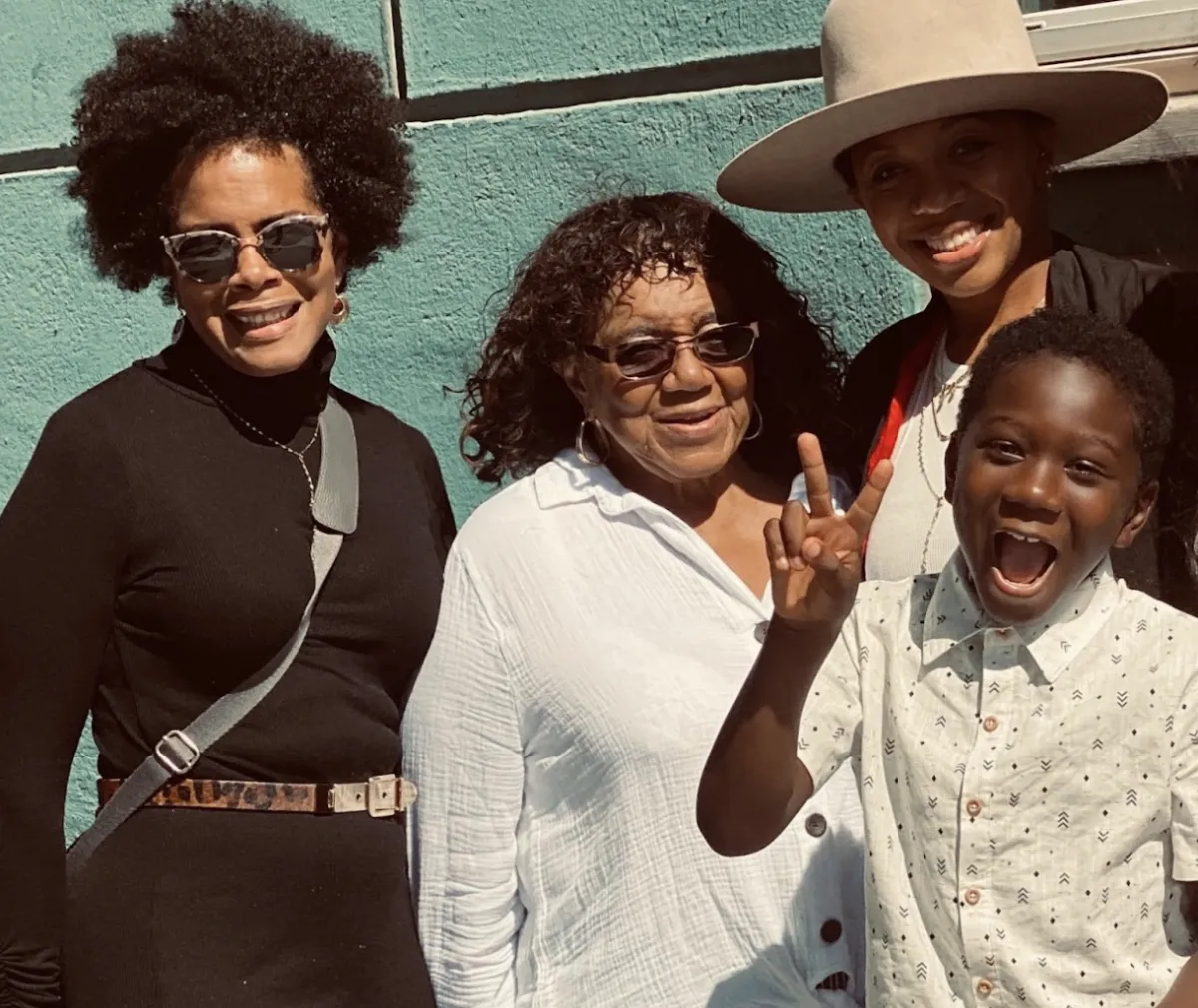

Maria Dowd, CEO of Dowd Solar Group
Maria joined ranks with Current Energy to promote clean, renewable energy to help residential and commercial property owners understand the value of producing their own electricity on-site, while reducing the reliance on increasingly expensive fossil fuels. Maria (in black), a native southern Californian, is Lula’s daughter (in white), mom of two daughters, grandmother of three, and cares tremendously about creating a cleaner planet for generations to come.
FREE GUIDE: 8 Things You Must Avoid When Shopping For Solar Panels
Enter your info below to continue
Connect With Me Online

Copyright © 2024 By DOWD SOLAR GROUP
Our Address:
8939 S Sepulveda Blvd,
Ste. 110-106
Westchester, CA 90045
